Categories
- Blog (65)
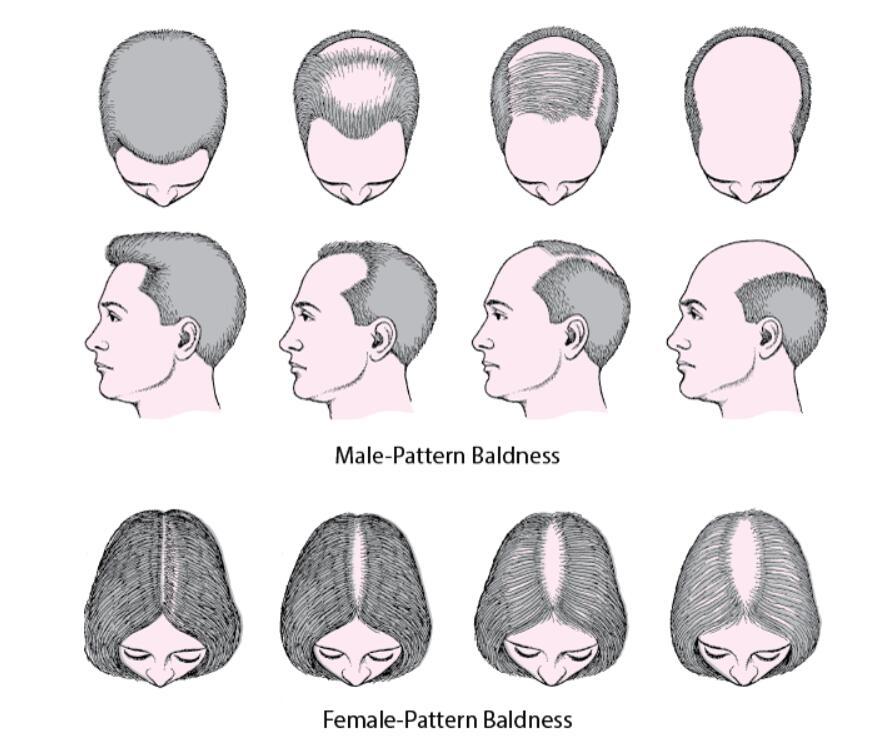
Androgenic alopecia is a common form of progressive hair loss characterize by a receding “M” hairline along with thinning hair in the area of the crown until it falls out completely and becomes baldness. Hair loss usually occurs gradually over a period of several years, but it can also start quickly. There are several common AGA pattern.
Classic male pattern baldness is severe hair loss and thinning in the temples and/or top of the head area, but will eventually affect the entire scalp. The severity of this type of receding hairline and baldness is measured on the Norwood scale.
Classic female pattern baldness occurs as hair thinning and hair loss becomes apparent in the middle of the scalp as the width of the hairline widens gradually. A more severe stage may manifest as diffuse hair thinning at the tip of the scalp, and the severity of this pattern of hair decline measure on the Ludwig scale or Savin scale.
Diffuse pattern baldness shows hair loss and thinning occurring throughout the scalp. So there is usually no obvious hairline decline and no specific pattern to measure. The result is a decrease in the density and volume of the hair.
It is also known as vertical slopecia. It usually manifests as thinning and shedding of hair on the sides of the head, appearing in a vertical fashion, moving from the bottom up.
The above is a summary of the common patterns of androgenic alopecia. However, when patients have androgenic alopecia, there is often not only one of these patterns of hair loss. These patterns of hair loss often mix together and appear in the same person at the same time.
In addition to the above androgenic alopecia, there are other non-androgenic alopecia, including loss of overall hair density caused by intense psychological or physical stress, alopecia areata, or hair loss caused by bacterial, fungal infections, or chemotherapy.
When you confirm your pattern hair loss as AGA, the most widely used medications are oral Finasteride and topical Minoxidil. Between Finasteride and Minoxidil, Finasteride usually prefer over Minoxidil, as the root cause of androgenic hair loss is androgens, and Finasteride targets androgens directly, slowing, stopping, and reversing the androgen-induced hair follicle miniaturization process at the root. Studies have shown that Finasteride and Minoxidil, when combined, are more effective than treatment with either drug alone.